简单粗暴,直接高效,这里不说WHAT和WHY,直接记录HOW。
添加maven依赖
1 | <dependency> |
IDEA Lombok plugin
入门级使用
1 | import lombok.Getter; |
Lombok注解说明
以下内容节选自 IT草根–Lombok开发指南
- val:用在局部变量前面,相当于将变量声明为final
- @NonNull:给方法参数增加这个注解会自动在方法内对该参数进行是否为空的校验,如果为空,则抛出NPE(NullPointerException)
- @Cleanup:自动管理资源,用在局部变量之前,在当前变量范围内即将执行完毕退出之前会自动清理资源,自动生成try-finally这样的代码来关闭流
- @Getter/@Setter:用在属性上,再也不用自己手写setter和getter方法了,还可以指定访问范围
- @ToString:用在类上,可以自动覆写toString方法,当然还可以加其他参数,例如@ToString(exclude=”id”)排除id属性,或者@ToString(callSuper=true, includeFieldNames=true)调用父类的toString方法,包含所有属性
- @EqualsAndHashCode:用在类上,自动生成equals方法和hashCode方法
- @NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor and @AllArgsConstructor:用在类上,自动生成无参构造和使用所有参数的构造函数以及把所有@NonNull属性作为参数的构造函数,如果指定staticName = “of”参数,同时还会生成一个返回类对象的静态工厂方法,比使用构造函数方便很多
- @Data:注解在类上,相当于同时使用了@ToString、@EqualsAndHashCode、@Getter、@Setter和@RequiredArgsConstrutor这些注解,对于POJO类十分有用
- @Value:用在类上,是@Data的不可变形式,相当于为属性添加final声明,只提供getter方法,而不提供setter方法
@Builder:用在类、构造器、方法上,为你提供复杂的builder APIs,让你可以像如下方式一样调用:
1
2
3
4
5
6Person.builder()
.name("Adam Savage")
.city("San Francisco")
.job("Mythbusters")
.job("Unchained Reaction")
.build();更多说明参考Builder
- @SneakyThrows:自动抛受检异常,而无需显式在方法上使用throws语句
- @Synchronized:用在方法上,将方法声明为同步的,并自动加锁,而锁对象是一个私有的属性$lock或$LOCK,而java中的synchronized关键字锁对象是this,锁在this或者自己的类对象上存在副作用,就是你不能阻止非受控代码去锁this或者类对象,这可能会导致竞争条件或者其它线程错误
- @Getter(lazy=true):可以替代经典的Double Check Lock样板代码
- @Log:根据不同的注解生成不同类型的log对象,但是实例名称都是log,有六种可选实现类
- @CommonsLog
Creates log = org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory.getLog(LogExample.class); - @Log
Creates log = java.util.logging.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class.getName()); - @Log4j
Creates log = org.apache.log4j.Logger.getLogger(LogExample.class); - @Log4j2
Creates log = org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager.getLogger(LogExample.class); - @Slf4j
Creates log = org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogExample.class); - @XSlf4j
Creates log = org.slf4j.ext.XLoggerFactory.getXLogger(LogExample.class);
- @CommonsLog
Lombok使用示例
val示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public static void main(String[] args) {
val sets = new HashSet<String>();
val lists = new ArrayList<String>();
val maps = new HashMap<String, String>();
//=>相当于如下
final Set<String> sets2 = new HashSet<>();
final List<String> lists2 = new ArrayList<>();
final Map<String, String> maps2 = new HashMap<>();
}@NonNull示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public void notNullExample(@NonNull String string) {
string.length();
}
//=>相当于
public void notNullExample(String string) {
if (string != null) {
string.length();
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("null");
}
}@Cleanup示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//=>相当于
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}@Getter/@Setter示例
1
2
3
4(AccessLevel.PUBLIC)
(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
private int id;
private String shap;@ToString示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11(exclude = "id", callSuper = true)
public class LombokDemo {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//输出LombokDemo(super=LombokDemo@48524, name=null, age=0)
System.out.println(new LombokDemo());
}
}@EqualsAndHashCode示例
1
2
3
4
5(exclude = {"id", "shape"}, callSuper = false)
public class LombokDemo {
private int id;
private String shap;
}@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor and @AllArgsConstructor示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
(staticName = "of")
public class LombokDemo {
private int id;
private String shap;
private int age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new LombokDemo(1, "circle");
//使用静态工厂方法
LombokDemo.of(2, "circle");
//无参构造
new LombokDemo();
//包含所有参数
new LombokDemo(1, "circle", 2);
}
}@Data示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17import lombok.Data;
public class Menu {
private String shopId;
private String skuMenuId;
private String skuName;
private String normalizeSkuName;
private String dishMenuId;
private String dishName;
private String dishNum;
//默认阈值
private float thresHold = 0;
//新阈值
private float newThresHold = 0;
//总得分
private float totalScore = 0;
}在IntelliJ中按下Ctrl+F12就可以看到Lombok已经为我们自动生成了一系列的方法。
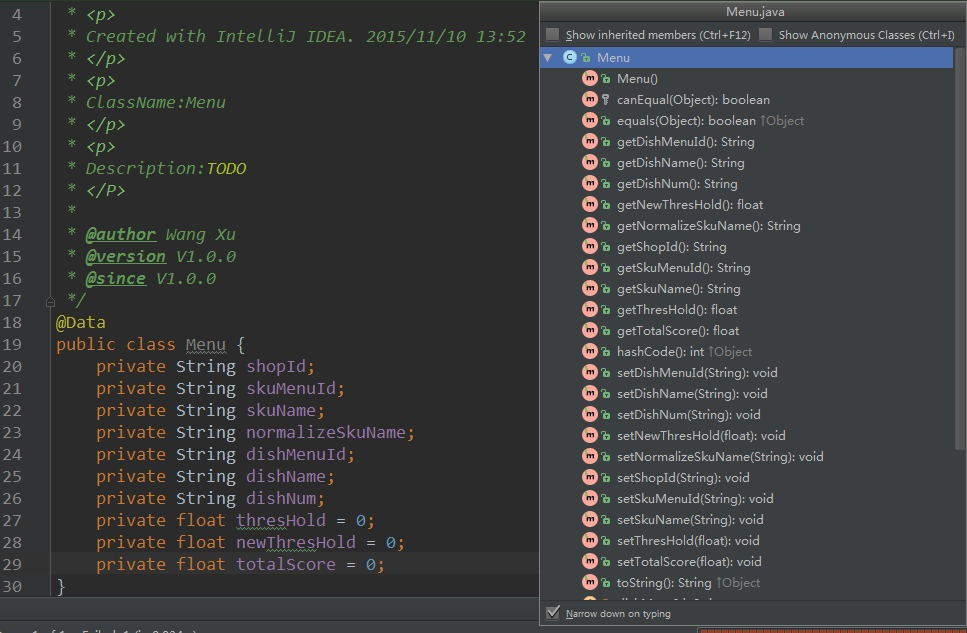
@Value示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class LombokDemo {
private int id;
private String shap;
private int age;
//相当于
private final int id;
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
...
}@Builder示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class BuilderExample {
private String name;
private int age;
private Set<String> occupations;
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuilderExample test = BuilderExample.builder()
.age(11)
.name("test")
.build();
}
}@SneakyThrows示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Test {
()
public void read() {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("");
}
public void write() {
throw new UnsupportedEncodingException();
}
//相当于
public void read() throws FileNotFoundException {
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("");
}
public void write() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
throw new UnsupportedEncodingException();
}
}@Synchronized示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public class SynchronizedDemo {
public static void hello() {
System.out.println("world");
}
//相当于
private static final Object $LOCK = new Object[0];
public static void hello() {
synchronized ($LOCK) {
System.out.println("world");
}
}
}@Getter(lazy = true)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class GetterLazyExample {
(lazy = true)
private final double[] cached = expensive();
private double[] expensive() {
double[] result = new double[1000000];
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = Math.asin(i);
}
return result;
}
}相当于如下所示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class GetterLazyExample {
private final AtomicReference<Object> cached = new AtomicReference<>();
public double[] getCached() {
java.lang.Object value = this.cached.get();
if (value == null) {
synchronized (this.cached) {
value = this.cached.get();
if (value == null) {
final double[] actualValue = expensive();
value = actualValue == null ? this.cached : actualValue;
this.cached.set(value);
}
}
}
return (double[]) (value == this.cached ? null : value);
}
private double[] expensive() {
double[] result = new double[1000000];
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
result[i] = Math.asin(i);
}
return result;
}
}